

The formal charges present in each of these molecular structures can help us pick the most likely arrangement of atoms.

We can draw three possibilities for the structure: carbon in the center and double bonds, carbon in the center with a single and triple bond, and oxygen in the center with double bonds:Ĭomparing the three formal charges, we can definitively identify the structure on the left as preferable because it has only formal charges of zero (Guideline 1).Īs another example, the thiocyanate ion, an ion formed from a carbon atom, a nitrogen atom, and a sulfur atom, could have three different molecular structures: NCS –, CNS –, or CSN –. We know from our previous discussion that the less electronegative atom typically occupies the central position, but formal charges allow us to understand why this occurs. To see how these guidelines apply, let us consider some possible structures for carbon dioxide, CO 2.
Calculating formal charge hcno how to#
In the previous section, we discussed how to write Lewis structures for molecules and polyatomic ions. Explain the concept of resonance and draw Lewis structures representing resonance forms for a given molecule.Use formal charges to identify the most reasonable Lewis structure for a given molecule.Compute formal charges for atoms in any Lewis structure.

We hope that you find a good answer and gain the knowledge about this topic of science.By the end of this section, you will be able to:
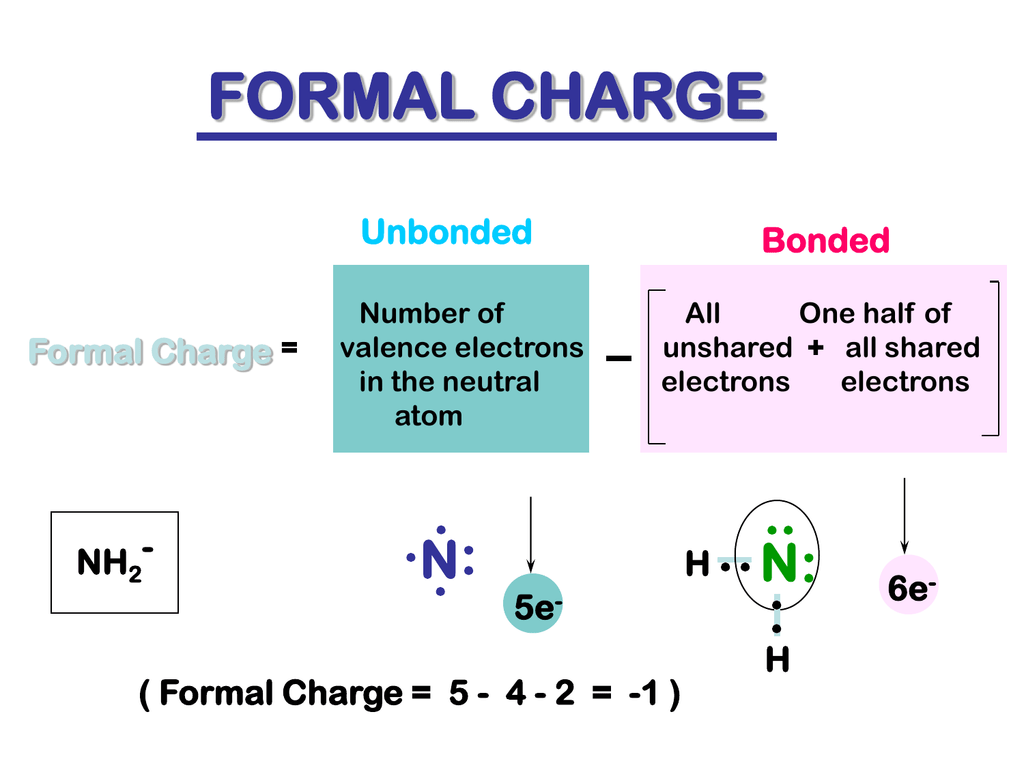
This is the resonance form C with a formal charge on every atom:įor $math_tag_14, the resonance form B is the preferred structureĪbove is the solution for “ Add formal charges to each resonance form of HCNO below., Please add formal charges for each…“. This is the Lewis structure for A resonance form: You can create a new resonance form by changing the electron pairs and bonds around an atom in a resonance format. A Lewis structure that has no formal charge on an atom is a favorable structure.Ī resonance form is any Lewis structure that exists for a molecule, ion or other substance. Non-bonding electrons can be placed on atoms in pairs.Ī molecule may have multiple Lewis structures. A triple bond is made using six electrons. Four electrons are required to form a double bond. Two electrons are required to form a single bond. The number of valence electrons within an atom is equal to its group number in a periodic table.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
